Blockchain smart contracts have the potential to revolutionize various industries by providing secure, transparent, and efficient solutions for complex transactions and processes.
Blockchain Smart Contracts; What Is A Smart Contract?
Smart contracts are computer programs that run on blockchain networks and execute automatically when specific conditions are met. This simple yet powerful concept holds significant implications across various industries. With each passing day, the list of smart contract use cases continues to expand as more individuals recognise the immense potential of this technology.
To illustrate with a real-world scenario, let’s consider the functioning of traditional contracts. Suppose an individual decides to rent a property, creating a contract between the tenant and the landlord. This contract meticulously outlines the rental agreement terms between the two parties, such as the obligation for the tenant to pay rent on the first day of every month. While a conventional contract can establish such terms, its enforcement typically relies on the involvement of a third party.
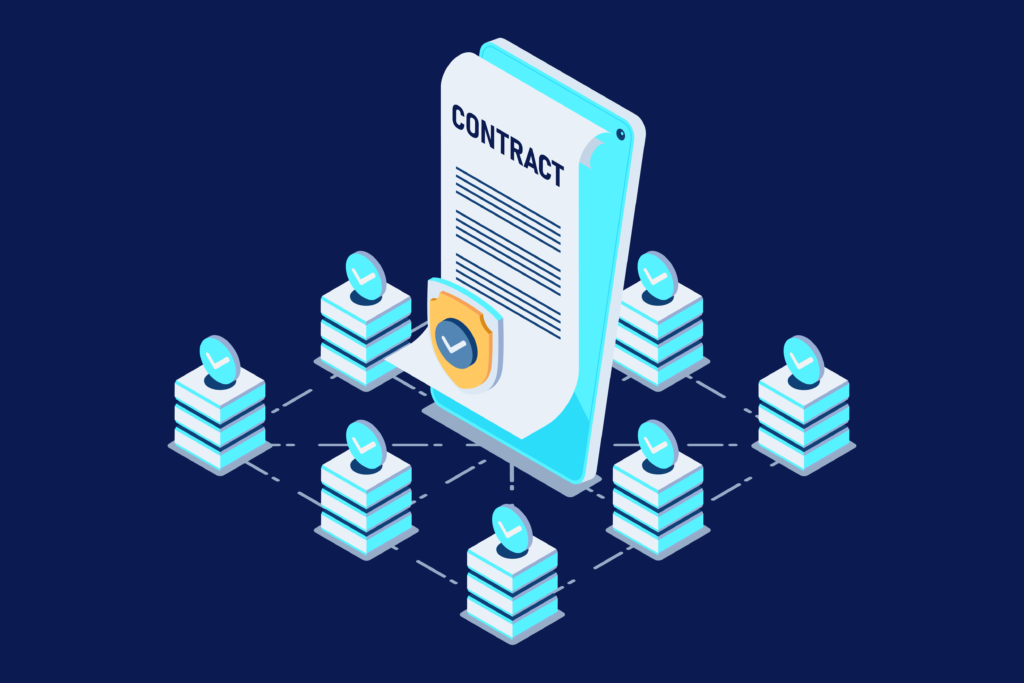

In situations where disputes arise between the involved parties, traditional contracts often require the intervention of a governmental third party. This third party may have participated in the contract’s creation in many instances. However, thanks to the advent of distributed ledger technology, the need for intermediaries to oversee contracts has become obsolete. The introduction of smart contracts has revolutionized numerous industries.
The concept of smart contracts was initially introduced in the 1990s by cryptographer Nick Szabo. He defined smart contracts as “a set of digitally specified promises, including protocols within which the parties execute these promises.”
Smart contracts are useful for several reasons:
Automation: Smart contracts automate the execution of contractual terms and conditions, eliminating the need for manual enforcement and reducing human error.
Transparency: The use of blockchain technology ensures transparency in smart contracts, as all transactions and actions are recorded and visible to all parties involved.
Security: Smart contracts utilise cryptographic techniques to ensure the security and integrity of the contract, making it tamper-proof and resistant to fraud.
Efficiency: Smart contracts streamline processes by removing the need for intermediaries, reducing paperwork, and expediting transaction settlement.
Cost Savings: With the elimination of intermediaries and manual processes, smart contracts can significantly reduce transaction costs, making them a cost-effective solution.
Versatility: Smart contracts have a wide range of applications across various industries, including finance, supply chain management, real estate, healthcare, and more.

Also, read: How To Get Crypto Airdrop
Real Smart Contract Use Cases
Now that the basic understanding of what a Smart Contract is, here are some use cases of smart contracts in various industries;
– Finance and Banking: Smart contracts can streamline financial processes such as loan origination, trade settlements, and cross-border remittances. They automate contract execution, ensure compliance, and reduce the need for intermediaries, leading to faster and more cost-effective transactions.
– Supply Chain Management: Blockchain smart contracts enable end-to-end visibility and traceability in supply chains. They automate supply chain processes, including inventory management, product provenance, and logistics, ensuring transparency and reducing fraud, counterfeiting, and supply chain disruptions.
– Healthcare: Smart contracts in healthcare facilitate secure and interoperable sharing of patient data between healthcare providers, insurers, and patients. They can automate claims processing, insurance verification, and patient consent management, improving efficiency and data privacy while reducing administrative costs.
– Real Estate: Blockchain smart contracts simplify property transactions by automating tasks like title transfers, escrow agreements, and rental agreements. They enable peer-to-peer transactions, reduce paperwork, and increase property ownership and management transparency.
– Intellectual Property Rights: Smart contracts can manage and protect intellectual property rights by automating royalty payments, licensing agreements, and copyright registration. They provide a tamper-proof record of ownership and ensure fair and transparent distribution of royalties.
– Energy and Utilities: Blockchain smart contracts enable peer-to-peer energy trading, where producers and consumers can directly trade energy without intermediaries. They ensure transparency in energy transactions, enable dynamic pricing and promote renewable energy integration into the grid.
– Voting and Governance: Smart contracts can revolutionise voting systems by providing secure, transparent, and auditable elections. They eliminate the possibility of tampering or manipulation, ensuring fair and accurate voting results.
– Insurance: Blockchain smart contracts automate insurance processes, including claims processing, policy management, and premium payments. They enhance trust between insurers and policyholders, simplify claims settlement, and reduce fraudulent activities.
These are just a few examples of how blockchain smart contracts can be applied across industries. The decentralized and automated nature of smart contracts provides immense potential for efficiency, transparency, and trust in various sectors, paving the way for innovative and transformative solutions.
The bottom line
If you’re considering integrating smart contracts into your organization, now is the perfect time to unlock their potential. The possibilities are limitless, and smart contracts offer many benefits for streamlining and optimising your operations. Let your imagination guide you as you discover the transformative power of smart contracts in revolutionizing your business processes.